Climate change continues to have profound impacts globally, with the Arctic region experiencing some of the most significant and visible effects. The Arctic's average temperature has risen at a rate nearly four times the global average, making it the fastest-warming region on Earth .
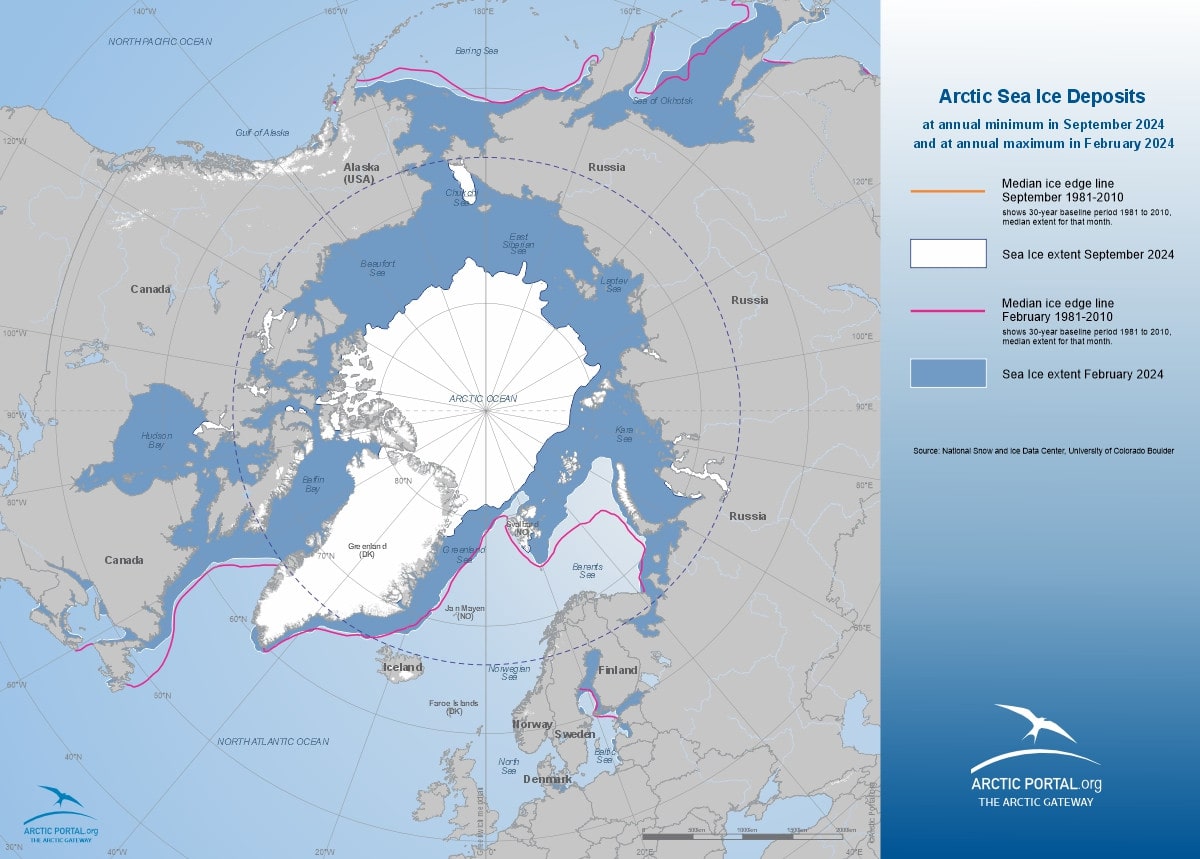 Arctic Sea Ice Decline
Arctic Sea Ice Decline
The extent of Arctic sea ice has been decreasing steadily. On September 11, 2024,the Arctic sea ice reached its annual minimum extent, measuring approximately 4.28 million square kilometers (1.65 million square miles). This marks the seventh-lowest extent recorded since satellite observations began in 1979 . The reduction in sea ice not only signifies a warming climate but also has cascading effects on global weather patterns and sea levels.
Implications for Shipping
The diminishing sea ice has opened new maritime routes in the Arctic, notably the Northern Sea Route. These routes offer shorter passages between Asia and Europe compared to traditional routes like the Suez or Panama Canals. However, increased shipping activity poses environmental risks, including potential oil spills and disturbances to marine ecosystems . Moreover, the infrastructure to support such routes is still developing, and the unpredictable nature of ice conditions presents navigational challenges.
Oil and Gas Exploration
Reduced sea ice has made previously inaccessible areas available for oil and gas exploration. Arctic oil and gas extraction are projected to increase by 20% over the next five years. While this presents economic opportunities, it also raises concerns about environmental degradation, especially given the fragile nature of Arctic ecosystems and the potential for oil spills in remote areas where response capabilities are limited.
However, the harsh and unpredictable conditions pose significant challenges. Extreme cold, shifting ice, and long periods of darkness complicate exploration, infrastructure development, and emergency response. Additionally, operating in such a remote region leads to higher costs and greater environmental risks, requiring specialized technology and international regulatory coordination.
Ecosystem Changes
The Arctic ecosystem is undergoing rapid transformations. Thawing permafrost has turned the tundra from a carbon sink into a carbon source, releasing significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere . Wildlife populations, such as polar bears and caribou, are declining due to habitat loss and changing food availability . These changes not only affect biodiversity but also the Indigenous communities that rely on these species for subsistence.
International Climate Agreements
Efforts to address climate change continue on the international stage. The 2024 UN Climate Conference (COP29) emphasized the urgency of limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C. Achieving this goal requires immediate and transformative actions, including significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions . The Arctic's rapid changes underscore the importance of global cooperation in mitigating climate impacts.